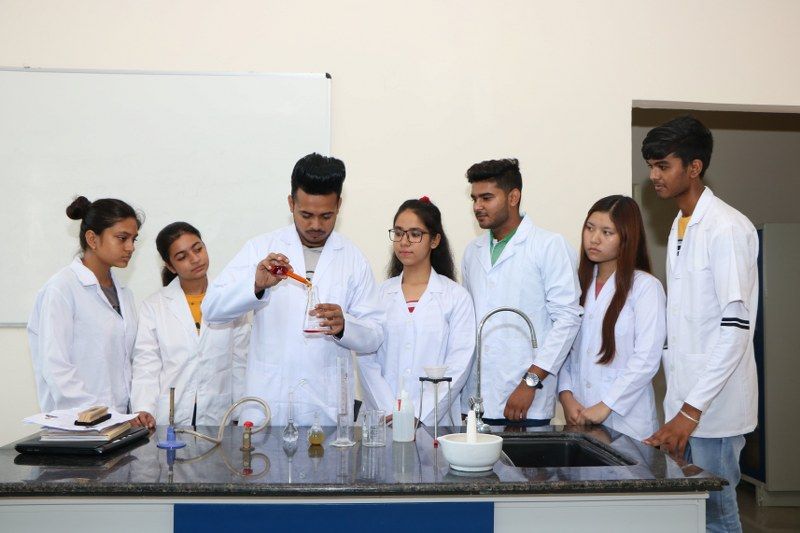

Pharmaceutical Sciences
CT University's School of Pharmaceutical Sciences (SOPS) is dedicated to advancing excellence in drug discovery and development, aiming to enhance community health through innovative research, education, and entrepreneurship.

SOPS strives to be globally recognized for excellence in drug discovery and development, focusing on community health and offering industry-oriented education with a global healthcare impact.
The school aims to provide transformative education that fosters interdisciplinary knowledge, leadership, and problem-solving skills. It emphasizes engaging with external partners to enrich the educational experience beyond traditional university boundaries.

UGC Recognised
CT University has obtained the recognition/approval of the Bar Council of India to run its Law programs under the School of Law. Approval by UGC under Section 2(f) of the UGC Act, 1956. Approval by UGC under Section 22 of the UGC Act, 1956.

25 Years Legacy
CT University owes its genesis to the establishment of the CT Educational Society in Jalandhar in the year 1997. After the legacy of more than 22 years, CTU was established in 2017 under the excelling vision of Sardar Charanjit Singh Channi, Chancellor, CTU.

rank of CT University in India?
CTU Overall ranking by IIRF is 133 out of 171 colleges in India in 2023 CTU is a widely recognised and awarded university in India. CTU has excelled in providing quality education across various disciplines and ranked 26 in the ARIIA Rankings

Placement Experience
There is excellent placements and job opportunities in CT University. Almost 75-80% of students get placed in many big firms. Major Co.s which visit the campus are TATA Motors, HDFC Bank, Mahindra & Mahindra, etc. The average package offered is around 5–10 lakhs.
RECRUITERS
ALUMNI
PLACEMENTS
HIGHEST PACKAGE OFFER

CT UNIVERSITY ORGANISES ‘PHARMACY AND HEALTHCARE JOB FAIR 2023’
CT University organised ‘Pharmacy and Healthcare Job Fair 2023’ in collaboration with DBEE. The event, brought together a multitude of students, esteemed companies, and renowned professionals, creatin...

Drosophila lab Inauguration
Dr. Bharti Mahajan inaugurated the state-of-the-art Drosophila Lab at SOPS, marking a significant step towards advancing genetic research and innovation in the field. The lab promises to be a hub for...

National Science Day
SOPS celebrated National Science Day by organizing engaging activities to honor scientific achievements and promote awareness of science in society. The event featured insightful discussions and inter...

Jab Aushadhi Diwas
SOPS celebrated Jan Aushadhi Diwas 2025, emphasizing the importance of affordable healthcare and access to quality medicines for all. The event highlighted the government's efforts in promoting the Ja...
CT University’s commitment to provide an environment for excellence in Research and Development in all disciplines is arguably the best. The spectrum of CTU research activities makes the academic environment very unique that brings out the best out of creative thinking and provides the pathway to boarding, supporting, and carving highly-skilled researchers.

10-03-2023
‘PHARMACY AND HEALTHCARE JOB FAIR 2023’
CT University organised ‘Pharmacy and Healthcare Job Fair 2023’ in collaboration with DBEE. The event, brought together a multitude of students, esteemed companies, and renowned professionals, creating a platform of unparalleled opportunities. The aim of Job Fair was to bridge the gap between aspiring students and leading companies in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors and provide a valu...

15-09-2023
CT UNIVERSITY ORGANISES ‘PHARMACY AND HEALTHCARE JOB FAIR 2023’
CT University organised ‘Pharmacy and Healthcare Job Fair 2023’ in collaboration with DBEE. The event, brought together a multitude of students, esteemed companies, and renowned professionals, creating a platform of unparalleled opportunities. The aim of Job Fair was to bridge the gap between aspiring students and leading companies in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors and provide a valu...
27-01-2025
Workshop on HPLC
SOPS organized a workshop on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), offering hands-on training and in-depth knowledge on advanced techniques. Participants gained practical insights into HPLC applications and its role in analytical research.

28-02-2025
Drosophila lab Inauguration
Dr. Bharti Mahajan inaugurated the state-of-the-art Drosophila Lab at SOPS, marking a significant step towards advancing genetic research and innovation in the field. The lab promises to be a hub for groundbreaking discoveries.

28-02-2025
National Science Day
SOPS celebrated National Science Day by organizing engaging activities to honor scientific achievements and promote awareness of science in society. The event featured insightful discussions and interactive sessions for participants of all ages.

05-03-2025
Jab Aushadhi Diwas
SOPS celebrated Jan Aushadhi Diwas 2025, emphasizing the importance of affordable healthcare and access to quality medicines for all. The event highlighted the government's efforts in promoting the Jan Aushadhi scheme to empower citizens.

10-03-2023
‘PHARMACY AND HEALTHCARE JOB FAIR 2023’
CT University organised ‘Pharmacy and Healthcare Job Fair 2023’ in collaboration with DBEE. The event, brought together a multitude of students, esteemed companies, and renowned professionals, creating a platform of unparalleled opportunities. The aim of Job Fair was to bridge the gap between aspiring students and leading companies in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors and provide a valu...

15-09-2023
CT UNIVERSITY ORGANISES ‘PHARMACY AND HEALTHCARE JOB FAIR 2023’
CT University organised ‘Pharmacy and Healthcare Job Fair 2023’ in collaboration with DBEE. The event, brought together a multitude of students, esteemed companies, and renowned professionals, creating a platform of unparalleled opportunities. The aim of Job Fair was to bridge the gap between aspiring students and leading companies in the pharmaceutical and healthcare sectors and provide a valu...

27-01-2025
Workshop on HPLC
SOPS organized a workshop on High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), offering hands-on training and in-depth knowledge on advanced techniques. Participants gained practical insights into HPLC applications and its role in analytical research.

28-02-2025
Drosophila lab Inauguration
Dr. Bharti Mahajan inaugurated the state-of-the-art Drosophila Lab at SOPS, marking a significant step towards advancing genetic research and innovation in the field. The lab promises to be a hub for groundbreaking discoveries.

28-02-2025
National Science Day
SOPS celebrated National Science Day by organizing engaging activities to honor scientific achievements and promote awareness of science in society. The event featured insightful discussions and interactive sessions for participants of all ages.

05-03-2025
Jab Aushadhi Diwas
SOPS celebrated Jan Aushadhi Diwas 2025, emphasizing the importance of affordable healthcare and access to quality medicines for all. The event highlighted the government's efforts in promoting the Jan Aushadhi scheme to empower citizens.
The best aspect of CT University is the fact that there are countless opportunities, groups and association, and that no matter who you are, there are people like you here. CT University students are amongst the most driven in the world, we study hard and accomplish big things in our academics, research and internships.

Ans.Pharmacology is the branch of medicine and biology that studies the effects of drugs on the body. It is essential in pharmaceutical sciences as it helps in understanding how drugs work, their side effects, and their therapeutic uses.
Ans.The curriculum typically covers topics like drug classification, drug mechanisms, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, toxicology, clinical pharmacology, and pharmacotherapeutics.
Ans.Pharmacokinetics involves the study of the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) of drugs in the body, while pharmacodynamics focuses on the effects of drugs on the body, including mechanisms of action.
Ans.Graduates can pursue careers in research, clinical pharmacology, drug regulatory affairs, drug safety, toxicology, pharmaceutical industry, academic teaching, and healthcare.
Ans.Common tools include animal models, cell cultures, computer simulations, spectrophotometry, chromatography, and various bioassays to study drug effects.
Ans.Pharmacology plays a key role in the drug development process by providing information on the safety, efficacy, and mechanisms of new drugs, which helps in designing better therapeutics.
Ans.Ethical considerations include animal welfare, informed consent in clinical trials, minimizing harm to participants, and ensuring the integrity of research findings.
Ans.Pharmacology helps in understanding how individual genetic differences affect drug responses, which is crucial for developing personalized treatment plans and optimizing drug therapy.
Ans.Toxicology is the study of the harmful effects of drugs and chemicals on living organisms. It is studied by examining dose-response relationships, organ-specific toxicity, and chronic versus acute effects of substances.
Ans.Pharmacology ensures that healthcare professionals understand the therapeutic uses, dosages, side effects, and interactions of drugs, enabling them to make informed decisions about patient care and medication management.
Ans.Pharmacognosy is the study of natural products, especially those derived from plants, animals, and microorganisms, used in medicine. It is important in pharmaceutical sciences because it helps in discovering and understanding bioactive compounds that can be developed into therapeutic drugs.
Ans.The main branches of pharmacognosy include plant pharmacognosy, animal pharmacognosy, microbial pharmacognosy, and the study of marine organisms. These branches focus on different natural sources of bioactive compounds.
Ans.Pharmacognosy focuses on the medicinal properties, uses, and safety of natural substances, while phytochemistry specifically deals with the chemical constituents of plants and their therapeutic properties.
Ans.Medicinal plants are classified based on their therapeutic uses, chemical constituents (e.g., alkaloids, flavonoids, terpenes), and botanical characteristics. They can also be classified into categories like herbs, spices, and other plant-based remedies.
Ans.Identification and evaluation of medicinal plants include techniques like macroscopic and microscopic examination, chromatographic methods (e.g., TLC, HPLC), spectroscopy (e.g., UV, IR, NMR), and biological assays for bioactivity.
Ans.Herbal medicines are used in treating a wide range of conditions, including digestive disorders, respiratory diseases, inflammation, pain management, and skin conditions, often as alternative or complementary therapies.
Ans.Natural products are isolated using solvent extraction, distillation, or chromatography. The compounds are then purified through various techniques like recrystallization, column chromatography, and high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC).
Ans.Pharmacognosy plays a crucial role in drug discovery by identifying bioactive compounds in natural sources, which can lead to the development of new medications. Many modern drugs are derived from natural products or inspired by them.
Ans.Challenges include standardization of herbal products, quality control, lack of clinical evidence, regulation and safety concerns, and variability in active compounds due to growing conditions and extraction methods.
Ans.Pharmacognosy encourages the sustainable use of natural resources, conservation of medicinal plants, and ethical sourcing of raw materials to prevent over-exploitation and ensure the continued availability of bioactive compounds for future generations.
Ans.Pharmacokinetics refers to the study of drug absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME), while pharmacodynamics deals with the study of drug effects and the mechanism of action in the body.
Ans.Pharmaceutics covers various drug delivery systems such as sustained release, controlled release, transdermal, targeted delivery, and nanoparticles for specific routes of administration.
Ans.The pH of the medium can influence the solubility of drugs, especially weak acids and bases, which in turn affects their dissolution rate and bioavailability.
Ans.Bioavailability refers to the extent and rate at which the active drug enters systemic circulation, affecting the drug's therapeutic efficacy. Formulation strategies aim to optimize bioavailability for effective treatment.
Ans.The first-pass effect refers to the metabolism of orally administered drugs by the liver before they enter systemic circulation, which may reduce the drug's effectiveness.
Ans.A solution is a homogenous mixture where the drug is fully dissolved in a solvent, while a suspension is a heterogeneous mixture where the drug particles are dispersed but not dissolved in the solvent.